
So, melt viscosity and intrinsic viscosity can be related to each other as well. It is clear that, the changes in molecular weight of a polymer with high entanglement, affect melt viscosity more than intrinsic viscosity.īoth equations (2) and (4) are related to the molecular weight.

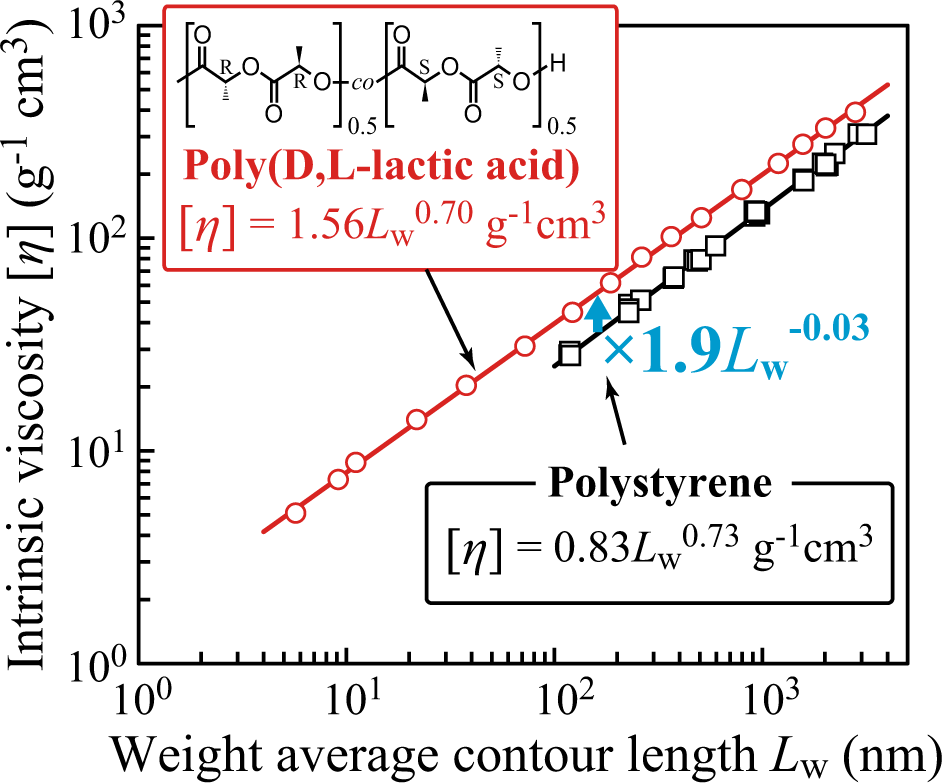
For most polymers the value of 𝛼 is within 0.5-0.8. Where 𝜂 is the intrinsic viscosity, and 𝐾՛ and 𝛼 are Mark-Houwink parameters and depend on a particular polymer-solvent system. On the other hand, Mark-Houwink equation defines the relationship between intrinsic viscosity of the polymer and its molecular weight as below Where 𝜂0 is zero-shear viscosity, and 𝐾 is a constant dependent on the polymer type. In a log form, the equation can be shown as

In polymers with high entanglement, the relationship between zero-shear viscosity and molecular weight is given by Fox-Flory equation as below Polymers with higher molecular weight have higher chain entanglement and this can lead to the increasing of shear viscosity or intrinsic viscosity. The reason is that, viscoelastic properties in polymer materials are dependent on molecular motion and chain entanglement. The idea behind this correlation was that both zero-shear viscosity and intrinsic viscosity can be related to the molecular weight of the polymer. However this characterization method involves with noxious solvents which may not be desirable.ĭynisco® LCR capillary rheometer series has a feature to provide correlation of shear viscosity data to the intrinsic viscosity of PET materials. As a result, IV parameter from dilute solution viscometer is not affected by the resin moisture content which removes the necessity of drying the samples before the tests. IV measurement is normally performed by dissolution of a small amount of the polymer in an appropriative solvent (e.g. Intrinsic viscosity however is commonly used among the PET manufactures as the specification of different resin grades. As a result, the melt flow rate (MFR) parameters of PET resins are strongly affected by their moisture level/drying condition and rarely provided by their suppliers. Normally, the moisture acts as a plasticizer and increases the flowability of the plastic melt. This has a huge effect on the flow behavior and rheological parameters of the plastic melt. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a hygroscopic resin from the polyester family which absorbs moisture onto their molecular structure when they are exposed to the ambient air. Correlation of Melt Viscosity of Polyethylene Terephthalate to Solution Intrinsic Viscosity Azadeh Farahanchi Ĭorrelation of melt viscosity of polyethylene terephthalate to solution intrinsic viscosity


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
